3. Release process and versioning
· 3 min read
Status
Accepted
Context
In order to deliver regularly the software to our users, we should implement a release process based on a predictable versioning scheme.
Versioning
A Release Version determines a distribution of determined node versions and underlying libraries.
- Our softwares must be able to interact seamlessly with other Mithril software.
- Our softwares must be able to be hosted on crates.io.
- Our softwares must clearly indicate compatibility with other Mithril components to end users.
Release process
A Release is a software package that is built once and then promoted from the testing environment to the production environment. It can be signed.
- Keep it simple.
- Automated as much as possible: all points not requiring human decision shall be automated.
- Minimize the mean time to release.
Decision
There are 3 versioned layers in the Mithril stack:
- HTTP API protocol to ensure compatibility in the communication between nodes (use Semver).
- Crate version: each node & library has its own version (use Semver). The commit digest is automatically added to the version by the CI pipeline.
- Release Version: the distribution version (use version scheme YYWW.patch | YYWW.patch-name). The VERSION file is computed by the pipeline from the tag release.
The documentation is tied to a Release Version.
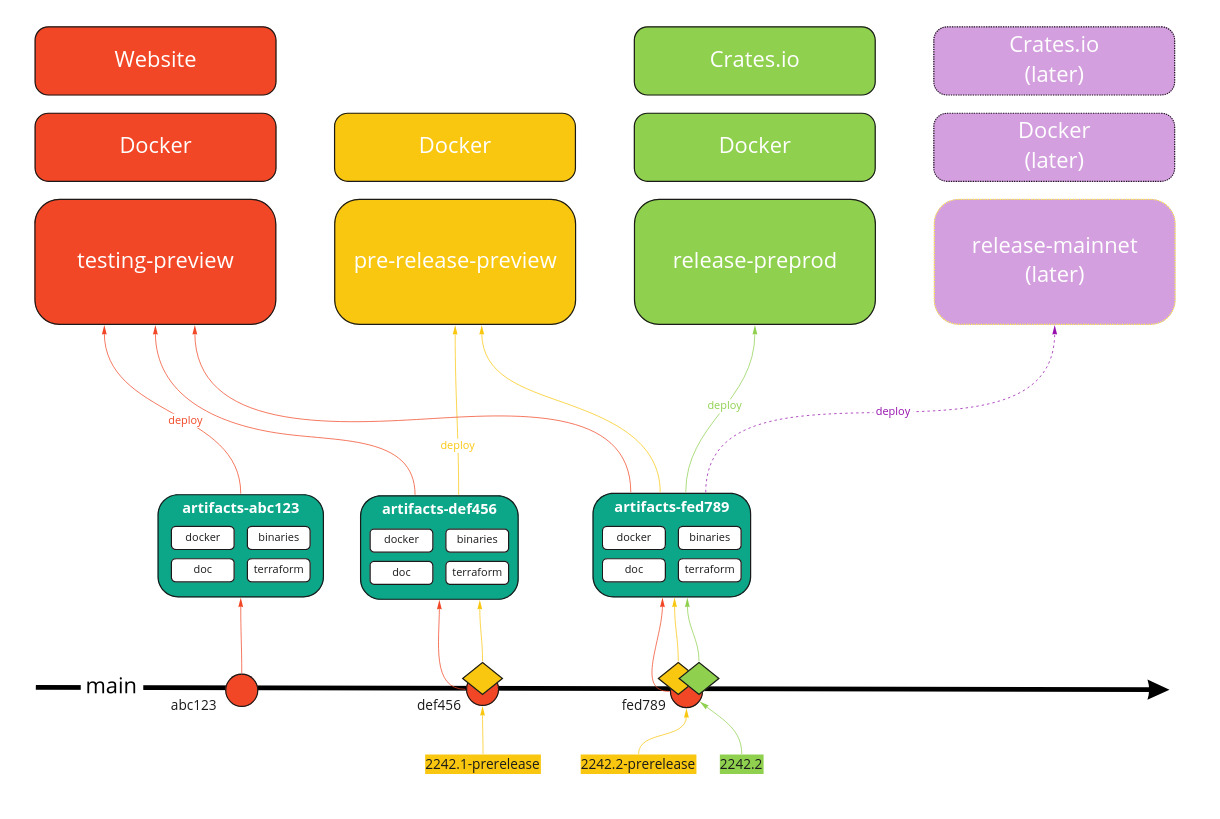
Release Process
Starting just after a new release has been made:
- Develop on a dedicated development branch.
- When merging PR on main: update the
Cargo.tomlfiles with version of the updated nodes. - Once merged, the CI creates an
unstabletag & release which is deployed on testing environment. - Push a tag using the distribution version format on this commit with a
-prereleasesuffix. - The CI gets the built artifacts associated with this commit and generates a named pre-release which is deployed on
pre-releasefor testing. - Push a tag using the distribution version format on this commit without the
-prereleasesuffix. - The CI gets the built artifacts associated with this commit and generates a named release which is deployed on
pre-releasefor testing. - In the release GitHub interface, edit the newly generated release, uncheck the
This is a pre-releasecheckbox. - The CI gets the built artifacts associated with this commit and generates a named release which is deployed on
release. - Create a commit:
- to promote the documentation website from future to current.
- to update the SQL schema with alterations from the previous release.
Hotfix Release
In case of a blocking issue (following a distribution release) on the release environment that requires an immediate fix:
- Create a branch on the last release tag with the following scheme:
hotfix/{last_distribution-version}.{last_patch_number + 1}. - Development of the fix is done on this branch.
- After each commit on this branch, the CI creates an
unstabletag & release which is not deployed on testing environment (testing must be done on an ad hoc environment manually created). - Push a tag on the branch last commit using the branch distribution version with a
-hotfixsuffix. - The CI gets the built artifacts associated with this commit and generates a named pre-release which is deployed on
pre-releasefor testing. - In the release GitHub interface, edit the newly generated release, uncheck the
This is a pre-releasecheckbox. - The CI gets the built artifacts associated with this commit and generates a named release which is deployed on
release. - Merge the hotfix branch on main branch (and adapt the changes if they are not compatible with the current main branch).